Molality - Freezing Point Lowering:
In dilute solutions, the lowering of the freezing point is
directly proportional to the number of solute molecules (or moles) in a given
weight of solvent. The effect of a nonelectrolyte dissolved in water can
be calculated by:
kf x m = DTf
(kf = molal F.P. constant for H2O
= 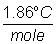 ) )
(m = molality of the
solution)
Then, the freezing point of the solution can
be calculated by: Freezing point of solvent -DTf
Example:
What is the freezing point of a solution containing 46.5 g
of ethylene glycol (MM = 62 g/mol) per 500 g (0.500 kg) of water?
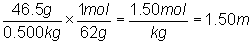
kf x m = 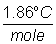 x
1.50 m = 2.79 oC = DTf x
1.50 m = 2.79 oC = DTf
F.P. of water - DTf
= 0.000 oC - 2.79 oC = -2.79
oC
Last modified
Contact us for more info

| 