Derivation of Gas Constant, R:
GO BACK
Choose any gas:
1
mole of Argon = 39.948 g Ar = 22.4
L Ar @ STP
STP = Standard
temperature (0oC or 273 K) &
Standard Pressure = 1 atmosphere
Assume the gas acts
ideally. Then PV = nRT
Solve
for R: 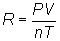
Substitute into
equation: 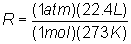
Solve: R
= 0.0821 atm L / mol K
If R is
needed in units of pressure (kPa):
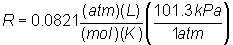 = 8.314 kPa L
/ mol K = 8.314 kPa L
/ mol K
If R is
needed in units of pressure (mm Hg)
= 62.396 mm Hg L / mol K
I would suggest always using the value
of 0.0821 atm L / mol K for R.
You must be sure the pressure you calculate
with in the problem is ALWAYS in atmosphere if using the
value
R = 0.0821 atm L / mol K.
R = 0.0821 atm L / mol K
8.314 kPa L / mol K
62.396 mm Hg L / mol K
Last modified
Contact us for more info

| 